Paper Outlines Approaches To Valuing Resilience
February 28, 2022
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
February 28, 2022
A new paper by the National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (NARUC) the National Association of State Energy Officials (NASEO), and Converge Strategies that details approaches to estimating the value of resilience.
The paper, Valuing Resilience for Microgrids: Challenges, Innovative Approaches, and State Needs, summarizes new approaches to valuing resilience that can be used by utilities and regulators and applied to proposed investments in microgrids and other resources.
While reliability has been measured for decades using widely accepted metrics, resilience, utilities, policymakers, and regulators have not agreed upon a universal definition of resilience.
In 2013, NARUC proposed a definition of resilience for state utility regulators and the White House released a definition focusing on critical infrastructure protection.
In 2018, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission put forward a definition. And in 2019 the National Renewable Energy Laboratory provided a definition that highlighted the importance of multi-stakeholder planning. To fill in the gaps, state regulators have also stepped in to provide their own definitions of resilience.
Although the definitions overlap, they differ in scope and specificity even though resilience has emerged as an important concept as utilities invest billions of dollars to strengthen generation, transmission and distribution infrastructure in the face of high-impact, low-frequency events, including extreme cold, droughts, heat waves, and cyber and physical attacks, the paper’s authors said.
“Developing tools and methods to accurately assess the costs and benefits of resilience investments is a critical step toward the goal of mitigating the impacts of outages on customers and society,” the paper said.
Traditionally, utility expenditures have been guided by “imprecise approaches that fail to account for the impacts of outages or anticipate” high impact low frequency events, the paper said. However, new approaches to analyzing the costs and benefits of resilience investments, such as microgrids, can enable more efficient use of ratepayer and taxpayer resources to deliver better outcomes, according to the paper.
In an effort to share practices and find common ground, state energy policymakers and regulators joined the NASEO-NARUC Microgrids State Working Group to explore benefits and costs of microgrids, identify challenges and barriers to microgrid development, and to share successful approaches.
And while the NARUC-NASEO paper was written with Microgrids State Working Group members in mind, the authors said it may be useful to utilities, emergency management agencies, community development organizations, municipal governments, and other stakeholders.
Specifically, the NARUC-NASEO paper summarized five new and pending resilience valuation approaches developed by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; the Edison Electric Institute and Commonwealth Edison; the National Renewable Energy Laboratory; Sandia National Laboratories and the University of Buffalo; and the Federal Emergency Management Agency.
NARUC and NASEO said they would continue “to promote sharing of knowledge across states and innovative approaches to common challenges in forums such as the NASEO-NARUC Microgrids State Working Group.”
“Future research may provide updates on resilient microgrid approaches in progress and on lessons learned from initial deployments,” the authors said.
Russian Cyber Threats: What You Need To Know
February 25, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 25, 2022
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) is offering resources and guidance related to cyber threats from Russia, which launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine on Feb. 24.
The Russian government “engages in malicious cyber activities to enable broad-scope cyber espionage, to suppress certain social and political activity, to steal intellectual property, and to harm regional and international adversaries,” CISA notes on its website.
Recent advisories published by CISA and other unclassified sources reveal that Russian state-sponsored threat actors are targeting a number of industries and organizations in the United States and other Western nations including energy, nuclear and water.
CISA notes that the same reporting associated Russian actors with a range of high-profile malicious cyber activity, including the 2020 compromise of the SolarWinds software supply chain, the 2020 targeting of U.S. companies developing COVID-19 vaccines, the 2018 targeting of U.S industrial control system infrastructure, and the 2017 NotPetya ransomware attack on organizations worldwide.
On Feb. 23, 2022, CISA, the United Kingdom’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), National Security Agency (NSA), and the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) released a joint Cybersecurity Advisory identifying that the actor known as Sandworm or Voodoo Bear is using a new malware, referred to as Cyclops Blink.
The NCSC, CISA, and FBI have previously attributed the Sandworm actor to the Russian General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate’s Russian Main Centre for Special Technologies.
CISA’s website includes a Russian malicious cyber activity section that lists all CISA advisories, alerts, and malware analysis reports on Russian malicious cyber activities.
“SHIELDS UP” Guidance
CISA is also offering what it refers to as “SHIELDS UP” guidance related to cybersecurity.
“CISA recommends all organizations — regardless of size — adopt a heightened posture when it comes to cybersecurity and protecting their most critical assets,” it said.
Recommended actions include:
- Reducing the likelihood of a damaging cyber intrusion
- Taking steps to quickly detect a potential intrusion
- Ensuring that the organization is prepared to respond if an intrusion occurs
- Maximizing the organization’s resilience to a destructive cyber incident
“Russia’s unprovoked attack on Ukraine, which has been accompanied by cyber-attacks on Ukrainian government and critical infrastructure organizations, may have consequences for our own nation’s critical infrastructure, a potential we’ve been warning about for months,” CISA said.
“While there are no specific or credible cyber threats to the U.S. homeland at this time, we are mindful of the potential for Russia’s destabilizing actions to impact organizations both within and beyond the region, particularly in the wake of sanctions imposed by the United States and our Allies. Every organization — large and small — must be prepared to respond to disruptive cyber activity,” it noted.
CISA, along with its partners in the U.S. Intelligence Community, law enforcement, the military, and sector risk management agencies, is monitoring the threat environment 24/7 to discern whether those threats manifest themselves in risks to the U.S. homeland.
In the wake of continued denial of service and destructive malware attacks affecting Ukraine and other countries in the region, CISA is working closely with its Joint Cyber Defense Collaborative (JCDC) and international computer emergency readiness team (CERT) partners to understand and rapidly share information on these ongoing malicious cyber activities.
The current environment “requires us all to be laser-focused on resilience. This must include a focus on ensuring preparedness and a rapid, coordinated response to mitigate the impact of such disruptions on our national security, economic prosperity, or public health and safety.”
CISA said it has been working closely with its critical infrastructure partners over the past several months to ensure awareness of potential threats, “part of a paradigm shift from being reactive to being proactive.”
As part of this effort, “we recognize that many critical infrastructure or state, local, tribal, and territorial governments find it challenging to identify resources for urgent security improvements.”
In response, CISA has established a catalog of free services from government partners, the open-source community, and JCDC companies to assist with this critical need.
President Biden Addresses Cybersecurity Threat In Remarks
On Feb. 24, President Biden said that if Russia “pursues cyberattacks against our companies, our critical infrastructure, we are prepared to respond.” He made his remarks in a speech at the White House.
“For months, we have been working closely…with the private sector to harden their cyber defenses, sharpen our ability to respond to Russian cyberattacks as well,” he said.
Last summer, the Department of Energy (DOE) reported that federal government agencies and the electricity industry had made significant strides in support of White House goals aimed at boosting the cybersecurity of critical infrastructure in the U.S.
In April 2021, the Biden Administration launched an Industrial Control Systems (ICS) Cybersecurity Initiative to meet its goal of strengthening the cybersecurity of the critical infrastructure across the country.
The initiative was kicked off with a 100-day action plan for the U.S. electricity subsector led by DOE’s Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER) in close coordination with CISA, and the Electricity Subsector Coordinating Council.
On July 28, 2021, President Biden further emphasized the importance of this initiative and broader cybersecurity efforts through his National Security Memorandum on Improving Cybersecurity for Critical Infrastructure Control Systems.
APPA Offers Cybersecurity Resources
The American Public Power Association (APPA) offers a wide range of resources on cybersecurity for its members, including a Cybersecurity Defense Community.
Those resources include, among other things, the Public Power Cyber Incident Response Playbook, which walks through the steps and best practices a utility can follow in the event it experiences a cyber incident or attack. APPA is also working with the Department of Energy to help deploy Operational Technology, or OT, cybersecurity sensors at member utilities.
Click here for additional information on APPA’s resources, or reach out to cybersecurity@publicpower.org to get involved.
Ditto Details Utility Sector’s Proactive Approach to Guard Against Cyberattacks
Among the many steps that the electricity sector takes to proactively guard against cyberattacks are tabletop exercises under which utility operators respond to a scenario and work through responses, said Joy Ditto, President and CEO of APPA, last October.
If such a scenario becomes a reality, “they have those lessons learned to apply,” Ditto said during a cyber summit held by the Aspen Institute.
Collaboration among the electric sector, government agencies and other industries plays a key role in the success of these exercises, Ditto pointed out.
FERC Moves To Close Gap In Reliability Standards For Electric Grid Cyber Systems
In January 2022, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) issued a notice of proposed rulemaking (NOPR) proposing to strengthen mandatory critical infrastructure protection (CIP) reliability standards by requiring internal network security monitoring for high- and medium-impact bulk electric system cyber systems.
The NOPR proposed to direct the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) to develop and submit new or modified reliability standards on internal network security monitoring to address what FERC regards as a gap in the current standards.
Incoming Chair Of APPA’s Policy Makers Council Details Key Advocacy Role That Council Plays
February 25, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 25, 2022
Jim Brooks, a City Council member for Evansville, Wis., and incoming Chair of the American Public Power Association’s (APPA) Policy Makers Council (PMC), recently detailed the key role that the PMC plays as a voice for public power in Washington, D.C.
“The PMC brings together about 40 elected officials from across the country whose main task is to call on Congress and policy writers in Washington to present the concerns of public power communities with a single voice,” Brooks said in a Q&A with Public Power Current.
“Lawmakers see swarms of paid lobbyists on a regular basis, but they know that when we show up, we are bringing along the thoughts and needs of thousands of voters in their district. Many in Congress started in local government and have maintained those ties to our communities, to our advantage,” he said.
Brooks noted that the Chair of the PMC works with APPA staff “to make sure that monthly calls bring the highest benefit to all the members and to make sure that future leadership of the Council keeps to the highest standards. I am looking forward to carrying on the work of so many before me.”
Brooks, who will formally take over as Chair of the PMC later this year, is attending APPA’s Legislative Rally in Washington, D.C., which starts on Feb. 28.
Wisconsin’s Evansville Light & Water, a small utility serving 4,700 customers, is advised by a Utilities Committee comprised of City Council members.
Brooks has served on the City Council since 2010 and has been president since 2013 and he also serves as the Utilities Committee chair.
Brooks also addressed the question of how important it is that the voice of smaller public power utilities, such as Evansville Water & Light’s, is heard through bodies such as the PMC.
“The PMC works as a leveler to make sure that the thousands of public power communities all have their voice heard by lawmakers,” he noted.
“Whether leading a utility with 300 people in the call-center or one with one person to answer the phones, send out bills, and do daily dispatch, we are all equal when we walk through the doors of the House office buildings to share our requests and ideas,” Brooks said.
“The needs of huge utilities may not be of the same magnitude as the smaller, but APPA — through the PMC — makes certain that we all have the opportunity to be heard.”
Meanwhile, Brooks was recently elected as chair of WPPI Energy’s Policy & Communications Leadership Council (PCLC).
WPPI Energy, based in Sun Prairie, Wisc., serves 51 locally owned electric utilities in Wisconsin, Iowa and Upper Michigan.
He noted that the PCLC coordinates efforts of the 51 member-owners of WPPI “to share a consistent message to our members and to our ratepayers. We meet quarterly to refine the messages we share across the membership.”
Over the past few years, “we have worked to streamline the quantity of daily and weekly communications to the membership while making them more impactful and tailored to the user. A daily digest of local news stories similar to APPA’s Public Power Current keeps leadership up to date while personalized power use and cost reports allow ratepayers to better understand their bills. And, a weekly digest delivers key WPPI business updates,” Brooks said.

Similarly, the PCLC works to shape the advocacy efforts in Madison, Wis., Lansing, Mich., and Des Moines, Iowa, as well as in Washington, Brooks said.
“We work with our government relations staff and with our state association to stay abreast of the goings on in the Capitol buildings and at the PSC and to share a consistent message as needed.”
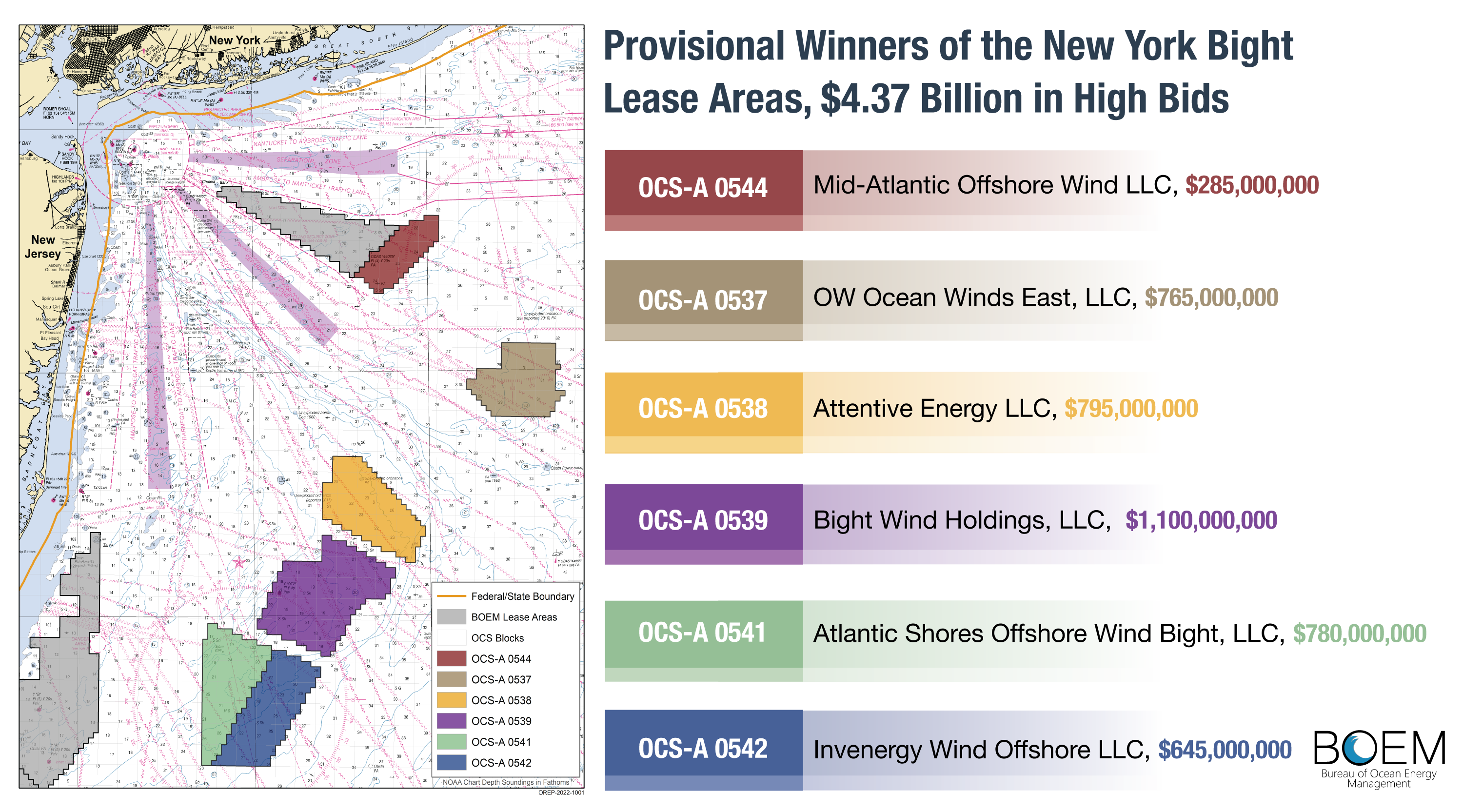
Offshore Wind Energy $4.37 Billion Lease Sale Is Highest Grossing Offshore Sale In History
February 25, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 25, 2022
The Department of the Interior (DOI) on Feb. 24 announced the results of the nation’s highest-grossing competitive offshore energy lease sale in history, including oil and gas lease sales, with the New York Bight offshore wind sale.
“These results are a major milestone towards achieving the Biden-Harris administration’s goal of reaching 30 gigawatts of offshore wind energy by 2030,” DOI said.
The lease sale offered six lease areas totaling over 488,000 acres in the New York Bight for potential wind energy development and drew competitive winning bids from six companies totaling approximately $4.37 billion.
Before the leases are finalized, the Department of Justice and Federal Trade Commission will conduct an anti-competitiveness review of the auction, and the provisional winners will be required to pay the winning bids and provide financial assurance to Interior’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management.
DOI said that the New York Bight offshore wind leases include innovative stipulations designed to promote the development of a robust domestic U.S. supply chain for offshore wind energy and enhance engagement with Tribes, the commercial fishing industry, other ocean users and underserved communities. The stipulations will also advance flexibility in transmission planning, it noted.
BOEM initially asked for information and nominations of commercial interest on 1.7 million acres in the New York Bight. Based on BOEM’s review of scientific data and extensive input from the commercial fishing industry, Tribes, partnering agencies, key stakeholders, and the public, BOEM reduced the acreage offered for lease by 72% to avoid conflicts with ocean users and minimize environmental impacts. BOEM will continue to engage with the public, ocean users, and key stakeholders as the process unfolds.
The Biden Administration has already approved the groundbreaking of the nation’s first two commercial-scale offshore wind projects in federal waters: the 800-megawatt Vineyard Wind project and the 130-megawatt South Fork Wind project.
BOEM expects to review at least 16 plans to construct and operate commercial offshore wind energy facilities by 2025, which would represent more than 22 gigawatts of energy.
In addition, this past fall DOI announced a new leasing path forward, which identified up to seven potential lease sales by 2025, including the New York Bight and offshore the Carolinas and California later this year, to be followed by lease sales for the Central Atlantic, Gulf of Maine, the Gulf of Mexico, and offshore Oregon.
North Carolina Utility Uses APPA Grant To Test Peak Shaving Batteries
February 24, 2022
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
February 24, 2022
Greenville Utilities Commission in North Carolina has added a 1-megawatt (MW) battery energy storage system (BESS) to its grid using a Demonstration of Energy & Efficiency Developments (DEED) grant from the American Public Power Association.
Greenville Utilities was looking for ways to reduce its coincident peak load. Historically the public power utility had used peaking plants, such as a reciprocating engine, for peak shaving. But under an agreement with Duke Energy Progress and North Carolina Eastern Municipal Power Agency (NCEMPA), Greenville Utilities has limits on how much load side generation it can add to its system.
“The allocation was set in the 1990s and was used up; we were looking at other alternatives,” John Worrell, Greenville Utilities’ director of electric systems, said.
Batteries do not count as generation, but Duke has pushed back on that view. In September 2020, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) sided with NCEMPA, allowing the joint action agency to use energy storage devices to reduce demand.
The pilot project was a good way to test the performance and economics of an energy storage system and compare it to the performance of a peak shaving engine, Worrell said. Greenville Utilities received financial assistance from the DEED program, which awarded the utility a $125,000 grant toward the total budgeted $1.6 million cost of the pilot project.
Construction on the project began in June 2020 and the battery came online in November 2020. The energy storage system includes a 1,000-kilowatt (kW), 2,250-kilowatt hour (kWh) lithium iron phosphate batteries.
The project required a year’s worth of data, so the pilot closed out last December. The DEED report was filed at the end of last month. The battery system, however, continues to operate and perform peak shaving duties for Greenville Utilities.
Overall, the project was a success, Worrell said, though there were some issues with batteries overheating, which in some instances restricted their availability during some peak periods. Those issues are being worked out with Powin, the manufacturer of the batteries, Worrell said.
The 12 months of data collected on the battery energy storage system showed that it consumed 106,191 kWh comprised of 33,921 kWh of auxiliary load and 72,207 kWh from charging events. The battery system discharged an average monthly peak supply of 965 kW with a max of 999 kW. A 1,000-kW discharge was recorded at 15-minute intervals but was not sustainable during a full hour as preferred.
Greenville Utilities serves about 71,000 electric customers with an average non-coincident peak demand of 301,500 kW and a coincident peak demand of 255,900 kW, consuming approximately 150 gigawatt hours monthly.
In terms of load management, the battery system operated 54 times for a total duration of 94.5 hours. The average duration per operation was approximately 1.76 hours with a maximum of 2.13 hours.
During the coincident peak hour, the battery system was able to discharge during 11 of 12 hours, resulting in an average monthly coincident peak load reduction of 779 kW with a maximum load reduction of 999 kW. The overheating issue affected total potential peak shaving capability for the months of May, June, August, and September.
Nonetheless, because it reduced monthly coincident peak demand, the battery system was able to avoid $218,743 in demand charges. The total expenses incurred operating the battery system were $43,414, resulting in an annual net savings of $175,328 with the ability to save approximately 62.4 percent of the total potential avoided demand charges.
The performance of the battery system ranked third among Greenville Utilities’ 12 peak shaving generators of various sizes in providing a high saving potential, according to the DEED report. The top ranked peak shaving generators were able to achieve 70.3 percent of total potential avoided cost. However, if the battery system’s average coincident peak load reduction of 779 kW were improved and equivalent to the average peak supply of 965 kW, the battery system would have ranked first with a saving potential of 82.2 percent, according to the DEED report.
Greenville Utilities said it plans to continue operating the energy storage pilot project for peak shaving applications because of the benefits it has provided in avoiding monthly coincident peak demand costs.
The utility also plans to continue to analyze the project to prepare for future projects as they arise. So far, Greenville Utilities is not considering installing another battery storage system. It is considering and has under discussion an energy storage tolling agreement.
Greenville Utilities did very well with the cost of its battery system, but that could be more difficult to replicate in the future because of rising costs, Worrell said. In addition, the cost of off-peak power to charge the batteries could go up as natural gas prices rise.
Alternatively, under a tolling agreement, a third party installs and owns the battery and the utility pays a set fee for peak shaving services. The agreements are usually based on coincident peak charges.
“If the toller takes the risk and we get a locked-in demand charge, we can hedge our peak demand over time, as long as the coincident peak from our supplier does not drop,” Worrell said. The agreement avoids the capital costs of installing a battery storage system while providing certainty of savings on coincident peak demand charges, he said.
Overall, Worrell said he would recommend using battery energy storage to reduce demand charges. Thanks to the pilot program, “we now know battery storage is a viable option with the same risks as a generator and just as reliable,” he said.
Members of APPA’s DEED Program can visit the Greenville project’s DEED Project Library page for access a useful Excel-based calculator which compares the financial feasibility of installing future BESS and RICE for peak-shaving applications, useful datasets containing hourly- and quarter-hourly performance data for Greenville’s BESS, photos, a spec sheet, and the full final report.
Greenville Utilities is a publicly owned utility in Pitt County that provides electric, water, sewer, and natural gas services to the City of Greenville and 75 percent of Pitt County. It is also the largest member of NCEMPA.
Massachusetts Municipal Wholesale Electric Company Launches Energy Efficiency Program
February 23, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 23, 2022
Massachusetts Municipal Wholesale Electric Company (MMWEC) recently launched a program that will replace residential, commercial and industrial energy efficiency programs in alignment with a shift in focus to a carbon-free future.
MMWEC’s energy efficiency programs, previously known as Home Energy Loss Prevention Services and Green Opportunity, have served MMWEC and its participating municipal light plants (MLPs) for more than three decades.
The driving purpose of the new NextZero brand is to help Massachusetts reach net zero carbon emissions by 2050.
MMWEC said that the new brand and its mission were developed through a rigorous strategic planning process with a subcommittee consisting of representatives of participating MLPs. The new mission emphasizes the critical role that community owned electric systems play in developing the clean energy future.
Municipal light departments participating in MMWEC’s residential energy efficiency programs through NextZero offer programs such as the “Connected Homes” demand response program, electric vehicle scheduled charging program, energy audits and rebates for energy-efficient appliances, electrification technologies and weatherization.
Several light departments also participate in commercial and industrial energy efficiency programs, including energy efficient lighting retrofits and customized efficiency upgrades.
Additional information about NextZero is available here.
MMWEC is a non-profit, public corporation and political subdivision of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts created by an act of the Massachusetts General Assembly in 1975 and authorized to issue debt to finance a wide range of energy facilities.
MMWEC provides a variety of power supply, financial, risk management and other services to the state’s consumer-owned, municipal utilities.
Legislation In Nebraska Proposes Nuclear Reactor Feasibility Study
February 22, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 22, 2022
Nebraska would use pandemic relief funds to conduct a feasibility study on siting options for nuclear reactors under a bill considered Feb. 16 by a Nebraska Senate Committee.
The bill, LB1100, would appropriate $1 million of the American Rescue Plan Act funds allocated to Nebraska to the state Department of Economic Development for use by a political subdivision that owns or operates a nuclear plant in the state to conduct a feasibility study.
The study would assess siting options for new, advanced nuclear reactors throughout Nebraska and existing electric generation facilities based on key compatibility assets for such reactors, according to the Nebraska Legislature’s Unicameral Update.
Daniel Buman, director of nuclear oversight and strategic asset management at Nebraska Public Power District (NPPD), testified in support of the proposal on behalf of NPPD and the Nebraska Power Association, which represents all of Nebraska’s public power utilities.
Calling a siting study the “next logical step” for meeting the state’s energy needs, he said a new generation of nuclear facilities could provide reliable, baseload carbon-free energy for the state.
Cooper Nuclear Station currently provides approximately 65 percent of the electricity for Nebraska customers over a rolling two-year average, he said.
“Siting studies are needed to identify the best combination of features and locations to maximize the value [of new nuclear sites] for Nebraska,” Buman said.
No one testified in opposition to the bill, which was introduced by Nebraska Sen. Bruce Bostelman, and the committee took no immediate action on LB1100.
Federal Energy Regulators Seek Answers Tied To Dynamic Line Ratings
February 22, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 22, 2022
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has launched an inquiry that seeks to answer a wide range of questions related to the use of dynamic line ratings (DLRs) on electric transmission lines.
Transmission line ratings represent the maximum transfer capability of each transmission line. These ratings can change based on weather conditions. The use of DLRs allows the capacity of a line to be updated regularly based on a wide range of weather and line-specific factors affecting the operation of electric transmission lines.
FERC’s Notice of Inquiry (NOI), which was issued on Feb. 17, builds on Order No. 881, which FERC approved in December of last year.
Order No. 881 directs transmission providers to use ambient-adjusted ratings (AARs) as the basis for evaluating near-term transmission service as well as for the determination of the necessity of certain curtailment, interruption or redispatch of near-term transmission service. AARs set transfer capability for transmission lines taking into account the effects of forecasted ambient air temperatures and the presence of solar heating.
Order No. 881 found that line ratings based on conservative assumptions about worst-case, long-term air temperature and other weather conditions can lead to underutilization of the transmission grid. Therefore, requiring all transmission providers to use AARs will better utilize the grid and help lower costs for consumers, FERC concluded.
Order No. 881 also acknowledged that transmission line ratings could be based on factors beyond forecasted ambient air temperatures and the presence of solar heating.
Applying these factors to reflect other weather conditions like wind, cloud cover, solar heating intensity and precipitation, as well as transmission line conditions such as tension or sag, could lead to greater accuracy and enable greater power flows, FERC said.
In addition, the Commission explained that the use of dynamic line ratings can detect situations where flows should be reduced for safe and reliable operation and to avoid unnecessary wear on transmission equipment.
FERC concluded in Order No. 881, however, that the record was insufficient to assess the relative benefits, costs and challenges of dynamic line rating implementation. In issuing the NOI, FERC is attempting to gather additional information on these issues.
The NOI seeks to further explore:
- Whether the lack of DLR requirements renders current wholesale rates unjust and unreasonable;
- Potential criteria for DLR requirements;
- The benefits, costs and challenges of implementing DLRs;
- The nature of potential DLR requirements; and
- Timeframes for implementing potential DLR requirements.
Initial comments in response to the NOI are due 60 days after publication in the Federal Register, with reply comments due 30 days later.
The NOI is available here.
DOE Unveils Organizational Realignment In Response To Infrastructure Law
February 22, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 22, 2022
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) recently announced an organizational realignment to ensure that it has the structure needed to effectively implement the clean energy investments in President Biden’s infrastructure law and the Energy Act of 2020.
The new organizational structure establishes two Under Secretaries: one focused on fundamental science and clean energy innovation and the other focused on deploying clean infrastructure.
The infrastructure law and the Energy Act of 2020 provide over $60 billion primarily for new major clean energy demonstration and deployment programs and more than triples DOE’s annual funding for energy programs, including significantly expanded research and development (R&D) and entirely new demonstration and deployment missions.
The Under Secretary for Infrastructure will focus on deploying clean energy solutions. The new Under Secretary will centralize existing offices focused on major demonstration and deployment with new offices. The existing offices moving to the new Under Secretary include DOE’s Loan Programs Office, Office of Indian Energy, Office of Clean Energy Demonstration, Office of Cybersecurity, Energy Security, and Emergency Response (CESER), and the Federal Energy Management Program.
Accompanying the announcement of the new Under Secretary is the launch of three new offices to support clean energy infrastructure deployment:
- The Grid Infrastructure Office to execute DOE’s Building a Better Grid initiative to modernize and upgrade the nation’s electric transmission lines and deploy cheaper, cleaner electricity across the country;
- The State and Community Energy Program to work more closely with states, localities, and communities to in the planning and deployment of decarbonization solutions;
- The Office of Manufacturing and Energy Supply Chains.
The offices in the Under Secretary for Science and Innovation (formerly the Undersecretary for Science and Energy) will drive research and development of energy technologies, with connected demonstration and deployment activities.
Through the realignment the Office of Science, DOE’s applied energy offices, and DOE’s 17 National Labs will continue their core discovery science and innovation missions including leveraging $12 billion in base appropriations as of fiscal year 2021 and $3.8 billion in funding in the infrastructure law and Energy Act of 2020.
FERC Revises Gas Pipeline Certificate Approach, Adopts New Gas Infrastructure GHG Policy
February 22, 2022
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
February 22, 2022
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) last week adopted a revised policy statement that significantly modifies its approach for considering new natural gas projects under the Natural Gas Act.
At the same time, FERC adopted an interim policy statement to explain how the Commission will assess the impacts of natural gas infrastructure projects on climate change in its reviews under the Natural Gas Act and the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
The Commission’s actions took place during its Feb. 17 monthly open meeting with a 3-2 vote occurring in both proceedings.
Updated Certificate Policy Statement (Docket No. PL18-1)
In 2018 and again, in 2021, the Commission issued notices of inquiry (NOI) seeking public comment on its 1999 policy statement on the certification of new interstate natural gas transportation facilities.
In particular, the Commission requested information on the consideration of the effects of such projects on affected communities, the treatment of precedent agreements in determining the need for a project, and the scope of the Commission’s environmental review, including an analysis of the impact of a project’s greenhouse gas emissions.
The updated certificate policy statement reaffirms many of the goals and objectives of the Commission’s 1999 policy statement, but further clarifies how the Commission will execute its public interest obligations under the Natural Gas Act.
The updated policy statement explains that, in making such determinations, FERC intends to consider all impacts of a proposed project, including economic and environmental impacts, together. It also calls for a robust consideration of impacts to landowners and environmental justice communities in the Commission’s decision-making process, FERC said.
And where the Commission traditionally has relied on precedent agreements between project applicants and shippers to establish the need for a project, the updated certificate policy statement states that applicants should provide more than just precedent agreements, to help explain why a project is needed, such as the intended end use of the gas.
It also states that the Commission may consider other evidence of need, including demand projections, estimated capacity utilization rates, potential cost savings to customers, regional assessments and statements from state regulators or local utilities.
Interim GHG Policy Statement (PL21-3)
The Commission said that it issued the interim GHG policy statement to explain how it will assess the impacts of natural gas infrastructure projects on climate change in its reviews under the National Environmental Policy Act and the Natural Gas Act.
FERC is seeking comment on all aspects of the interim policy statement, including, in particular, the approach to assessing the significance of the proposed project’s contribution to climate change.
The guidance is subject to revision based on the record developed in this proceeding. However, the Commission will begin applying the framework established in this policy statement in the interim.
This will allow the Commission to evaluate and act on pending applications under section 3 and section 7 of the Natural Gas Act without undue delay and with an eye toward greater certainty and predictability for all stakeholders, it noted.
The interim policy sets a threshold of 100,000 metric tons per year of GHG emissions. Projects under consideration with emissions above that level will require the preparation of Environmental Impact Statements (EIS).
The Commission will consider proposals by project sponsors to mitigate all or part of their projects’ climate change impacts. The Commission may condition its approval on further mitigation of those impacts.
In quantifying GHG emissions, FERC will consider emissions that are reasonably foreseeable and have a reasonably close causal relationship to the proposed action. This will include GHG emissions from construction and operation of the project, and may include GHG emissions resulting from the upstream production and downstream combustion of transported gas.
Applicability
As policy statements, neither document establishes binding rules.
They are intended to explain how the Commission will consider applications for natural gas project construction. They will apply only to pending and new projects; those applicants with projects now pending before the Commission will have the opportunity to supplement their records.
Commissioners Christie And Danly Dissent
Commissioners Mark Christie and James Danly dissented from both items.
In his dissent, Christie said it is a truism that FERC is an economic regulator, not an environmental regulator. “This Commission was not given certification authority in order to advance environmental goals; it was given certification authority to ensure the development of natural gas resources and their availability – this includes pipeline infrastructure – at just and reasonable rates,” Christie said,
“To construe the Commission’s analysis of the public convenience and necessity as a license to prohibit the development of needed natural gas resources using the public interest language in the NGA [Natural Gas Act] would be to negate the very legislative purpose of the statute,” he argued.
“To those who say ‘well, times have changed and Congress was not thinking about climate change when it passed the NGA,’ here’s an inconvenient truth: If Congress wants to change the Commission’s mission under the NGA it has that power; FERC does not,” wrote Christie.
He further argued that FERC’s actions “rely to a remarkable degree on a smattering of statements from a handful of recent orders. Simply put, these authorities are simply ‘too slender a reed’ to support the great weight today’s orders place on them.”
For his part, Danly said in his dissent of the updated policy statement on certification of new interstate natural gas facilities that the Commission’s jurisdiction and the public convenience and necessity standard are not as broad as the updated policy statement suggests. He also said that a number of the changes to the certificate policy statement are misguided.
As for the interim GHG policy statement, Danly said in his dissent of the policy statement that it is “irredeemably flawed.”
He said it is “practically unworkable because it establishes a standardless standard. Its universal application to all projects, both new and pending (some for over two years), is an affront to basic fairness and is unjustifiable, especially in light of the many unnecessary delays already suffered by applicants.”
Moreover, Danly argued the policy statement is unlawful “because it is illogical, it arrogates to the Commission power it does not have, and it violates the NGA, NEPA and the Commission’s and the Council on Environmental Quality’s (CEQ) regulations.”
