BPA On Path To Join Western Energy Imbalance Market In March 2022
September 27, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 27, 2021
After more than three years of rigorous review and analysis, the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) has decided to join the Western Energy Imbalance Market (EIM) in March 2022, BPA said on Sept. 27.
Participation in the California Independent System Operator’s (CAISO) Western EIM is expected to further enhance the value of the Northwest’s federal power and transmission system, BPA noted.
“This decision aligns with Bonneville’s strategic plan and opens up an opportunity to increase revenues through additional sales of surplus power and to reduce costs through greater efficiencies,” said BPA Administrator John Hairston in a statement. “As the West moves rapidly to decarbonize the grid, Western EIM participation will help us navigate future challenges and leverage opportunities to benefit our customers and the Northwest.”

BPA will now sign a Western EIM Entity Agreement as well as the remaining participation agreements with CAISO. CAISO will file the signed agreements with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission for approval. BPA plans to begin its final testing stage — parallel operations — on Dec. 1, 2021.
BPA is currently completing the work to implement new systems and processes to enable participation in the Western EIM beginning March 2022. The internal preparations are on-track and testing with the ISO has already begun.
Beginning in fall 2021, BPA will continue to hold implementation workshops to work through changes for customers, which will include informal and formal settlements training, and provide updates on BPA’s implementation efforts.
“Western EIM participation is a great introduction to emerging markets in the west,” said Hairston. “We hope to build on this experience to assess future market-based opportunities.”
As BPA assessed participation in the Western EIM, discussions about other industry improvements and market opportunities also emerged, BPA noted.
BPA plans to take part in the development of other markets and opportunities and will make decisions about its participation in these efforts through additional public processes.
One such opportunity is the Western Resource Adequacy Program organized by the Northwest Power Pool.
BPA proposed in a draft decision posted August 20 to participate in the next non-binding phase of this effort in which parties will test the design concepts, determine the program’s viability and shape its final design.
This is a first step at establishing common resource adequacy measurements and definitions.
In addition to participating in the Western Resource Adequacy Program, BPA is closely monitoring the potential formation of day-ahead markets in the West.
Both CAISO and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) have presented initial concepts that could provide additional opportunities and benefits for BPA and its customers, BPA said.
SPP manages the electric grid across 17 central and western U.S. states and provides energy services on a contract basis to customers in both the Eastern and Western Interconnections.
Information on BPA’s decision to join the Western EIM can be found at www.bpa.gov/goto/eim.
The Western EIM footprint currently includes portions of Arizona, California, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming, and extends to the border with Canada.
CAISO on Sept. 15 signed an implementation agreement with the Western Area Power Administration Desert Southwest region to participate in CAISO’s real-time energy market in 2023.
California Governor Signs Offshore Wind Legislation Into Law
September 27, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 27, 2021
California Gov. Gavin Newsom recently signed into law a bill that directs state agencies to develop a strategic plan for offshore wind resources in California.
Newsom on Sept. 23 signed into law AB 525 by Assemblymember David Chiu.
Under the new law, the California Energy Commission (CEC) has until June 1, 2022, to evaluate and quantify the maximum feasible capacity of offshore wind “to achieve reliability, ratepayer, employment, and decarbonization benefits and shall establish megawatt offshore wind planning goals for 2030 and 2045.”
The law also calls for the CEC, in coordination with the California Coastal Commission, Department of Fish and Wildlife, Ocean Protection Council, and State Lands Commission, to work with stakeholders, other state, local, and federal agencies, and the offshore wind energy industry to identify suitable sea space for wind energy areas in federal waters sufficient to accommodate the offshore wind planning goals.
In May 2021, the Biden administration, in conjunction with Newsom, announced an agreement identifying regions off the California coast that could support the administration’s goal of deploying 30 gigawatts (GW) of offshore wind energy by 2030.
According to a recent report, California has enough offshore wind power potential to meet 157% of the state’s 2019 electricity use.
RFP Seeks Partner To Develop Large-Scale Pumped Storage Project In California
September 26, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 26, 2021
The San Diego County Water Authority this month issued a request for proposals seeking a full-service private partner capable of developing a large-scale pumped energy storage project planned jointly by the Water Authority and the City of San Diego.
In July 2021, the San Vicente Energy Storage Facility received $18 million in the state budget signed by California Gov. Gavin Newsom, enough to advance the project through initial design, environmental reviews, and the federal licensing process.
The project could store 4,000 megawatt-hours per day of energy (500 megawatts of capacity for eight hours).
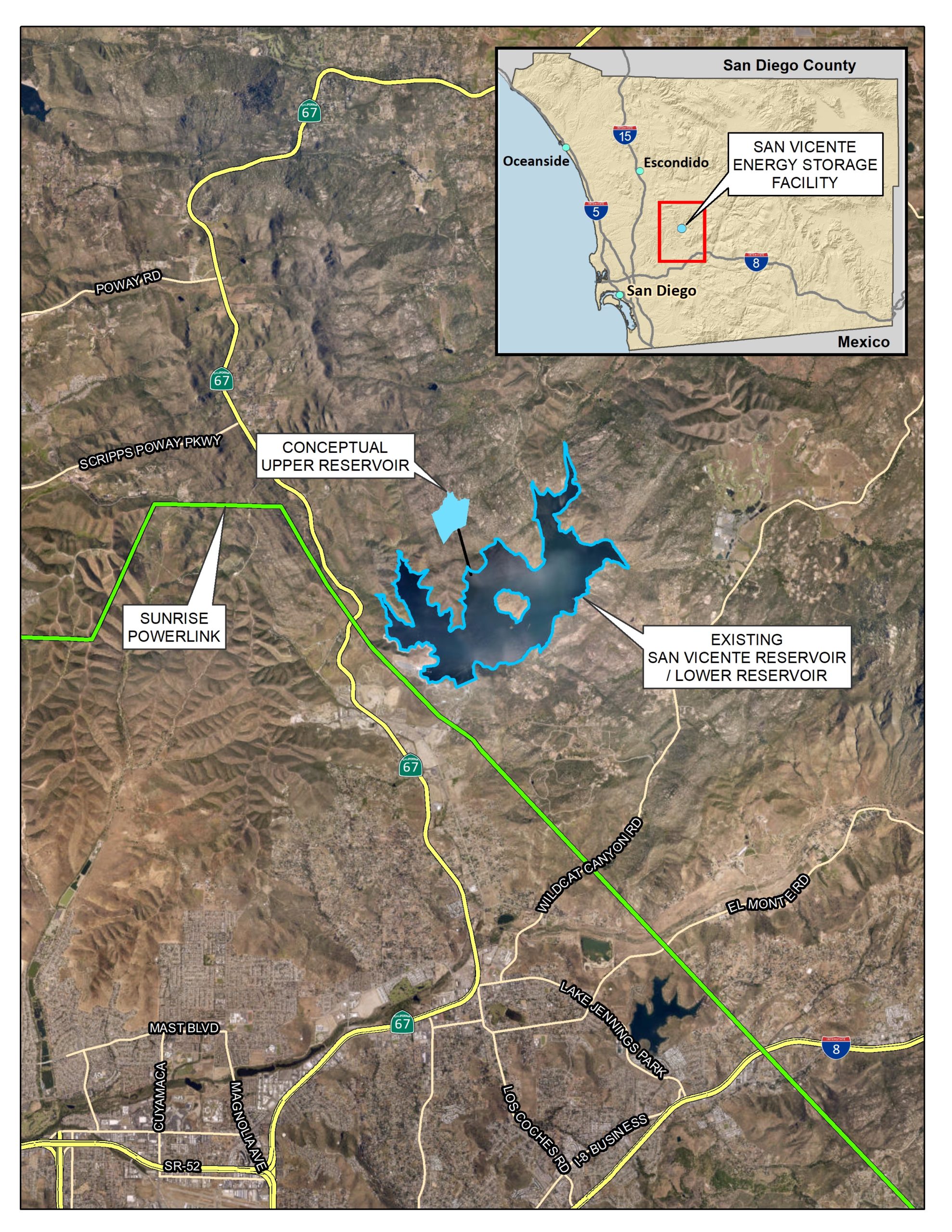
The potential project would create a small upper reservoir above the San Vicente Reservoir, along with a tunnel system and an underground powerhouse to connect the two reservoirs. The powerhouse would contain four reversible pump turbines.
The reservoir is near major electricity transmission interconnection facilities, which would allow the project to play a central role in integrating solar and wind energy from across the Southwest for use in San Diego County.
During off-peak periods, turbines would pump water to the upper reservoir where it would act as a battery of stored potential energy. During high energy use, the system would discharge energy as water from the upper reservoir flows downhill through the turbines. The exchange between the two reservoirs would not consume water and is closed-loop.
Proposals are due Nov. 3 and the RFP is available at: sdcwa.org/contracting-opportunities.
Lakeland Electric Installing Gas-Fired Generator To Replace Retired Coal Unit
September 25, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 25, 2021
Lakeland Electric is building a 120 megawatt (MW) natural gas-fired generator on land owned by the Florida city to replace a recently retired, coal-fired plant.
The reciprocating internal combustion engine (RICE) is being supplied by MAN Energy Solutions, which will install the machine on the brownfield site. MAN has committed to a fast-track delivery of the equipment by July 2022.
The engine uses a heat recovery system designed to support the plant’s stand-by operation and “perfectly matches Lakeland Electric’s stated commitment to safely provide its customers with affordable, highly dependable, and sustainable electric services,” Wayne Jones, chief sales officer at MAN Energy Solutions, said in a statement.
The new engine has an efficiency rating of more than 50 percent, even at partial loads, and will contribute to Lakeland Electric’s commitment to improve the carbon dioxide footprint of its power generation fleet, Jones said. MAN will maintain the plant under a service agreement for the next 10 years.
In December, Lakeland Electric announced plans to close Unit 3 of its McIntosh coal-fired plant, which it owned with the Orlando Utilities Commission, which has a 40 percent stake.
Lakeland Electric found that the coal generator was requiring increasingly expensive repairs while showing declining efficiency and unreliable performance. In addition, the large inventory of coal required to run the unit burdened the public power utility with a multi-million dollar risk should the unit fail.
At the time, Lakeland Electric said it would use its other natural-gas, diesel, and solar power generation capacity along with demand management, interruptible load, and power purchase agreements until replacement capacity could be built.
As part of its NextGen plan, Lakeland Electric plans to add five natural gas-fired internal combustion engines and increase its solar power and battery storage capacity by 2024.
The new natural gas generators will be more efficient and better able to manage the capacity fluctuations of solar power, Lakeland said, putting it on track to reduce its carbon dioxide emissions by 67 percent since 2001.
Project in S.C. Will Add Renewable Natural Gas To Public Power Utility’s System
September 25, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 25, 2021
The Greenwood Commissioners of Public Works in South Carolina is participating in a project that will create renewable natural gas for use in the public power utility’s gas distribution system.
Construction of the project at the Twin Chimneys Landfill site in Honea Path, South Carolina, began earlier this month. It is being built by Enerdyne Power Systems based in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Enerdyne Power Systems is part of The Landfill Group, which works in partnership with LS Power, a development, investment and operating company focused on the power and energy sectors.
The project will use landfill gas, a byproduct of decomposing waste, that will be collected at the Twin Chimneys site and converted into renewable natural gas that will be injected into the natural gas system owned and operated by the Greenwood Commissioners of Public Works.
When in commercial operation, expected by fourth-quarter 2022, the Twin Chimneys Power Producers (TCPP) project is expected to initially produce approximately 1,200 million metric British thermal units (MMBtu) of renewable natural gas per day.
Eventually, the project is expected to be capable of producing about 3,000 MMBtu per day.
All development, construction and operations of the project will be managed by other Landfill Group companies.
“We are excited to be a part of this first in the state project for a local gas company to receive processed landfill gas directly into its system for distribution to customers,” Jeff Meredith, general manager of Greenwood Commissioners of Public Works, said in a statement. “This project has truly been a collaborative effort between Greenville County, TCPP and Greenwood [Commissioners of Public Works] to make a positive impact on the environment and provide value to the customers we serve.”
The environmental benefits of the Twin Chimneys project are equivalent to reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by more than 28 million gallons of gasoline, according to Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) analysis, LS Power said in a statement.
Currently there is not a standard definition of renewable natural gas (RNG), according to the EPA, which developed it as a term of art for its voluntary RNG projects.
Biogas, such as landfill gas, has a methane content of between 45 and 65 percent and must be converted to renewable natural gas through a series of steps, including removing moisture, CO2, trace contaminants, and reducing nitrogen and oxygen content, to bring the methane content up to 90 percent or greater. Typically, renewable natural gas injected into a natural gas pipeline has a methane content between 96 and 98 percent, according to the EPA.
The benefits of using renewable natural gas include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving local air quality, boosting the local economy, and promoting fuel diversity, the EPA says.
“This project represents a major economic investment in Greenville County that will result in a significant reduction in CO2 emissions,” Michael Frixen, sustainability coordinator for the City of Greenville, said in a statement. He noted that Greenville is developing a new sustainability plan that will identify strategies to reduce the city’s CO2 emissions and overall environmental footprint.
EIA Sees Industrial Sector Natural Gas Consumption Rising Throughout 2021
September 25, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 25, 2021
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) expects industrial sector natural gas consumption in the U.S. to rise throughout 2021 and to exceed pre-pandemic 2019 levels.
The projection is based on EIA’s September Short-Term Energy Outlook, EIA said on Sept. 24.
“We forecast the growth to continue into 2022, and natural gas delivered to industrial consumers will average 23.8 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) that year. If realized, this amount would be near the current record high for annual industrial natural gas consumption set in the early 1970s,” EIA said.
It noted that many industrial processes have limited or no alternatives to natural gas for use as both fuel and feedstock, making industrial natural gas consumption relatively insensitive to short-term price fluctuations. “Some value-added industrial products such as ammonia, methanol, and hydrogen that are produced from natural gas remain economically competitive even when natural gas prices are relatively high,” it said.
U.S. industrial natural gas consumption averaged 22.9 Bcf/d in the first half of 2021, according to EIA’s Natural Gas Monthly.
Natural gas consumption fell in the U.S. industrial sector during 2020 when a drop off in U.S. economic activity led to a decline in output among industries that consume natural gas, such as the metals, petroleum and coal products, paper, and chemicals industries.
EIA said in its latest Short-Term Energy Outlook that it expects natural gas consumption in the U.S. industrial sector to average 23.5 Bcf/d in the second half of this year and 23.2 Bcf/d for 2021.
If realized, this amount of industrial natural gas consumption would exceed the 2019 average of 23.1 Bcf/d and mark the most U.S. industrial natural gas consumption since 1997.
Village of Pioneer, Ohio, Administrator Al Fiser Receives AMP Award
September 25, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 25, 2021
Al Fiser, village administrator for the Village of Pioneer, Ohio, is the 2021 recipient of the American Municipal Power (AMP) Seven Hats Award.
The AMP Seven Hats Award, which is modeled after the American Public Power Association’s (APPA) national Seven Hats Award, was initiated in 1984 to recognize utility managers who serve smaller communities of less than 2,500 meters, and whose management duties extend well beyond the scope of a manager in a larger system.
Award winners show skill in seven areas: planning and design, administration, public relations, field supervision, accounting, personnel or employee direction, and community leadership.
The award was presented to Fiser during the 2021 AMP Annual Conference, which took place Sept. 20–22 in Columbus, Ohio. Awards were also given to individuals and communities in the categories of electric system sustainability, innovation, public power promotion, safety and system improvement.
The Village of Pioneer is a small community located in northern Williams County, Ohio. Fiser has served the Village of Pioneer for 12 years.
With a small team of eight, Fiser led the completion of more than $18 million in infrastructure projects, including storm drainage, water treatment, power distribution and transmission projects, and more, all while he represented the village on the local economic board, school board and park board.
In nominating Fiser, Pioneer Mayor Ed Kidston noted that he is known for rolling up his sleeves on behalf of his employees and the village.
Click here for a video about the AMP Seven Hats Award and Fiser’s accomplishments.
APPA Seven Hats Recipients Featured on Public Power Now Podcast
Four APPA 2021 Seven Hats Award recipients have been guests on APPA’s Public Power Now podcast in recent months: Robert LaFave, Village Manager, Village of L’Anse Electric Utility, L’Anse, Michigan, Joe Price, Village Administrator, Grafton Village Power & Light, Grafton, Ohio, Faith Willoughby, Town Manager, Town of Chalmers, Indiana, and Jamie Lindstrom, Superintendent, Town of Argos, Indiana.
Click here to access the podcast episodes.
AMP Conference Celebrated Value of Public Power, Addressed Industry Trends
The 2021 AMP Annual Conference provided attendees (in-person and virtually) with a full schedule of sessions led by industry experts and leaders and celebrated the organization’s 50th anniversary.
Following AMP President and CEO Jolene Thompson’s opening remarks, participants welcomed APPA President and CEO Joy Ditto, Transmission Access Policy Study Group Executive Director Terry Huval and Large Public Power Council President John Di Stasio for a panel discussion about the value of public power and the key issues impacting the industry.
On day two, conference participants heard from Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Commissioner Allison Clements, PJM Interconnection President and CEO Manu Asthana, and Midcontinent Independent System Operator CEO John Bear for a panel discussion on the current power industry challenges and projections of the future, as well as the federal perspective on regional transmission organizations and markets.
The conference covered timely topics and trends in the power industry, including updates on power markets, a session on workforce development, a panel discussion about electric vehicles, and a discussion about “What Customers Really Want.”
In addition to the many sessions and events, AMP held its General Membership Meeting on Sept. 21.
During the AMP General Membership Meeting, elections were held for four expiring at-large AMP Board of Trustees seats. The AMP member communities of Bryan, Montpelier, Oberlin and Orrville were re-elected to three-year terms.
Following the General Membership Meeting, the AMP Board of Trustees met to elect officers for the coming year. The following individuals were re-elected to leadership positions: Chair – Jeff Brediger, City of Orrville, Ohio; Vice Chair – Robert Patrick, City of Wadsworth, Ohio; Secretary – Dave Carroll, City of Paducah, Ky.; Treasurer – Chris Monacelli, City of Westerville, Ohio.
EPA Proposes Guidance On Cleanup Of PCB-Containing Disaster Waste Post-Hurricane Ida
September 24, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 24, 2021
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recently proposed guidance related to the cleanup of Poly-Chlorinated Biphenyl (PCB)-containing disaster waste in the wake of the destruction of property resulting from Hurricane Ida.
The guidance was proposed by EPA Regions III,IV, and VI.
The EPA has routinely issued these guidance documents on clean up PCBs after a significant storm.
The guidance from Region III, which covers the states of Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Virginia, Maryland, Delaware and the District of Columbia, is effective through October 30, 2021.
The guidance from EPA Region IV, which covers the states of Mississippi, Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and six Tribal Nations is effective through October 31, 2021.
The guidance from Region VI, which covers the states of Louisiana, Texas, Arkansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma and 66 tribal nations, is effective through November 15, 2021.
The guidance applies to PCB remediation wastes, which contain PCBs as a result of spills, releases, or other unauthorized disposals, with specified limitations on PCB concentrations and disposal dates.
PCB remediation wastes include, but are not limited to, contaminated environmental media, such as soil and gravel, buildings and other man-made structures, such as concrete floors, wood floors, and walls contaminated from leaking transformers containing PCBs at or over 50 ppm.
Cleanup and disposal of PCB wastes can be based on the as-found concentrations in the spill materials for actions taken directly in response to conditions caused by the hurricanes when it is not possible to determine the spill source concentration at a site readily.
Cleanup activities in response to the hurricanes may occur beyond the 24-48 hour required spill response time period as circumstances require for the duration of the adverse conditions.
The guidance also includes a disposal option for PCB bulk product waste.
EPA has developed an interactive mapping tool of 12 types of recyclers and landfills that manage disaster debris. The tool can be used by disaster response, recovery, and planning experts to advance the safe recovery, recycling, and disposal of disaster debris. Click here to access the tool.
WPPI Energy Celebrates Commissioning of 100-Megawatt Solar Project
September 24, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 24, 2021
State and local leaders recently joined executives from NextEra Energy Resources LLC and WPPI Energy to celebrate the commissioning of the Point Beach Solar Energy Center, Wisconsin’s newest large-scale solar energy project.
The Point Beach Solar Energy Center spans 465 acres in the town of Two Creeks, Wis., and is adjacent to the Point Beach Nuclear Plant, which is also owned by a subsidiary of NextEra Energy Resources.
The Point Beach Solar Energy Center features more than 315,000 photovoltaic solar panels and has a capacity to generate 100 megawatts.

A subsidiary of NextEra Energy Resources built, owns and will operate the project.
The energy will serve WPPI Energy member communities under a 20-year power purchase agreement.
“Not only will Point Beach Solar provide affordable energy to our member communities, but it will also further diversify our portfolio and help us continue to reduce the carbon dioxide emissions associated with supplying power,” said Mike Peters, president and CEO of WPPI Energy.

With the addition of Point Beach Solar Energy Center, the WPPI Energy membership is on track for approximately a 45% reduction in carbon dioxide emissions by 2025 when compared to 2005.
Over the next 20 years, the Point Beach Solar Energy Center is expected to generate nearly $8 million in additional revenue for Manitowoc County, Wis., WPPI noted.
Member-owned, not-for-profit WPPI Energy serves 51 locally owned electric utilities.
NextEra Energy Resources is one of the largest wholesale generators of electric power in the U.S., with approximately 21,900 MW of net generating capacity, primarily in 37 states and Canada as of year-end 2019. NextEra Energy Resources is a subsidiary of Juno Beach, Florida-based NextEra Energy, Inc., an investor-owned utility.
Omaha Public Power District Weighs Potential Of Undergrounding Lines
September 23, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 23, 2021
Omaha Public Power District (OPPD) is in the midst of a comprehensive review of undergrounding its power lines.
The review began earlier in 2021 but its importance was underscored July 10 when a severe thunderstorm left 188,000 customers of the Nebraska public power utility without electricity.
Initially, the study was a way to evaluate least-cost methods of construction for new and rebuilt facilities. OPPD has studied undergrounding in the past, but “as materials and construction methods evolve it’s a good effort to revisit,” Guy Lucey, manager of distribution engineering at OPPD, said via email.
“Comparing the entire life-cycle cost of overhead and underground facilities gives direction on how OPPD should move forward as our system continues to grow,” Lucey said. “Initial studies have shown that there are cases where underground cable has a lower lifecycle cost than overhead conductor.”
Lifecycle includes the upfront cost of installation, maintenance over the expected life, tree trimming costs, locate costs, attachment income, outage performance, and cost to replace in the future.
The undergrounding study draws on different areas of the utility. “We approached it from many different directions including Engineering, Planning, and Maintenance,” Mike Herzog, manager of distribution planning at OPPD, said via email. As the project expanded into more of a case study approach, “our Land Rights team was specifically engaged to bring in their expertise,” Herzog said. “This ended up being a really critical step because it established that areas of the service territory may have differing levels of documentation.”
The review applies to all neighborhoods and portions of the system, but areas of particular impact are the more established parts of OPPD’s service territory that tend to be built with overhead construction and now have mature trees and landscaping.
“Almost all new residential and commercial developments in our metro areas are being constructed underground,” Lucey said. “We’re really looking to understand what underground facilities would look like in dense areas that were initially constructed with overhead facilities.”
OPPD is approaching the undergrounding cautiously. It can be expensive, and it is not always a cure-all solution. The study is still in its early stages but, as expected, “the upfront capital cost and resource commitment to execute something looks to be very high,” Herzog said. A large-scale rollout of undergrounding “would represent a significant commitment by OPPD over a decade or more,” he said.
In addition, areas that are hit hardest during severe weather are also the areas where burying existing overhead lines would be the most difficult, Herzog said. Those tend to be older, established neighborhoods with mature vegetation, landscaping, sheds, pools, patios, and other obstacles that have to be worked around.
OPPD is also looking at other options to boost reliability. “We increased our tree-trimming budget and have programs in place to make improvements on circuits that haven’t been performing as well,” Lucey said.
OPPD is aiming to have a summary of the undergrounding study by year end, which would enable the results to be included in OPPD’s Grid Modernization Strategic Initiative “The expectation is that this work will also continue to become an integrated part of our normal T&D practices,” Herzog said. “As technology continues to improve and construction methods may change, we want to build a framework where we can continue to reevaluate the long-term cost and benefit of multiple solutions to provide the best overall service to our customers,” he said.
“The expectation is that we will have guidelines, especially around new construction, but also looking at existing construction,” Lucey said. “New facilities going in as overhead have traditionally been identified as the least cost method. But with the improvements in cost and durability, we’re initially finding that there are some circumstances where underground facilities are the better economic choice.”
