Vermont Public Power Supply Authority Solar Array Located At Former Auto Salvage Yard
September 9, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 9, 2021
Vermont Public Power Supply Authority (VPPSA) and Encore Renewable Energy on Sept. 9 announced the commissioning of a new 2.1-megawatt (MW) community solar array located at a former auto salvage yard.
The project was developed as part of a partnership between Encore Renewable Energy and the VPPSA to develop, finance, and construct approximately 10 MW of solar capacity on behalf of VPPSA’s municipal utility members.
The project is expected to produce approximately 3,200,000 kilowatt hours per year. “The landowners will remain on the land that has been in their family for generations, as the operational solar project affords both an annual lease payment as well as the means to complete the environmental remediation required to address the regulatory approval for operation of a solar array on the former auto salvage facility which served the local community for decades,” VPPSA said.
This is the third solar array to be energized and the second project under a VPPSA and Encore Renewable Energy public-private partnership.
All generation from Salvage Yard solar will be sold to Vermont electric utilities that are not already 100% renewable.

VPPSA and Encore have arranged to build a 10 MW solar portfolio together with projects sited across multiple VPPSA member utility territories. Under the partnership, Encore performs all design, development, financing, and construction of solar projects, while VPPSA manages the resulting electric generation and maximizes its value for its member utilities’ communities.
The ground beneath the solar array is being planted with pollinator-friendly ground cover to support vital habitat for bees, butterflies, hummingbirds, moths, and other insects critical to future food security. In addition, pollinator friendly ground cover increases carbon sequestration, improves soil quality, reduces stormwater runoff, and channels storm water back into underlying aquifers, while addressing the social importance of supporting healthy food systems.
VPPSA provides municipal electric utility members with a broad spectrum of services and solutions, including regulatory assistance, financial planning, and power supply.
VPPSA members include Barton Village, Village of Enosburg Falls, Hardwick Electric Department, Village of Jacksonville Electric Company, Village of Johnson Electric Department, Ludlow Electric Light Department, Lyndonville Electric Department, Morrisville Water & Light Department, Town of Northfield Electric Department, Village of Orleans, and Swanton Village Electric Department.
Ann Arbor, Mich., City Council Approves Resolution On Public Power Feasibility Study
September 9, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 9, 2021
The Ann Arbor, Mich., City Council on Sept. 7 approved a resolution that asks the Ann Arbor Energy Commission to provide a recommendation on whether or not the Commission believes the city should undertake a feasibility study to understand options related to creating a municipal utility, including traditional and non-traditional models.
Prior to the council’s meeting, Ann Arbor, Mich., Council Member Elizabeth Nelson announced plans to introduce a resolution at the meeting asking the Ann Arbor Energy Commission to consider and vote on the question of a public power feasibility study for the city. She wanted the Energy Commission to vote on the matter at the Energy Commission’s Sept. 14 meeting.
At the city council meeting, Council Member Travis Radina noted that the Energy Commission is scheduled next month to hear from representatives of Boulder, Colo., and Winter Park, Fla., about their experiences related to municipalization.
In November 2020, Boulder voters declined to pursue municipalization for the city. Winter Park formed a public power utility in 2005.
Radina therefore put forth an alternative proposal that provided the Energy Commission with additional time to report back to the council.
But Nelson objected to the notion that her resolution “is somehow overstepping and dismissing the value” of input from the Energy Commission, noting that she has had many conversations with members of the Energy Commission who shared with her the length of time that this has been discussed.
“This is not a big step that I’m asking for,” she said. “I have crafted this resolution very carefully to include the Energy Commission. I would argue that if our community felt very strongly about this, if our community felt a compelling need,” the council could act “without first asking for input from the Energy Commission. My resolution is specifically asking for their input, with the knowledge that they have been discussing this for months.”
Nelson said that “I think that there is a reason to act sooner rather than later, and I know that members of our community are looking ahead to the possibility of this feasibility study informing a potential ballot question for next year and so three months might matter. Pushing this down the road three months – I don’t see any reason. I feel like the Energy Commission could probably give us an answer given that they’ve been talking about this since February.”
The council ultimately voted to ask the Energy Commission to provide a recommendation no later than December 31, 2021 as to whether or not the Commission believes the city should undertake a feasibility study to understand options related to creating a municipal utility, including traditional and non-traditional models.
The American Public Power Association offers a wide range of resources and information related to municipalization on its website.
Fitch Revises Outlook On LIPA To Positive, Cites Improved Leverage Ratio
September 8, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 8, 2021
Fitch Ratings recently revised its outlook on the Long Island Power Authority (LIPA) from Stable to Positive, with the rating agency saying the Positive Outlook reflects LIPA’s improved leverage ratio and Fitch’s expectation that the deleveraging trend that began in 2015 will continue through 2025.
“Debt has been a stakeholder concern since LIPA acquired the investor-owned Long Island Lighting Company in 1998,” said Tom Falcone, LIPA’s Chief Executive Officer. “The Board adopted a plan in 2015 to reduce LIPA’s leverage and the cost of debt. That plan has saved customers over $500 million and achieved four upgrades of LIPA’s bond ratings,” he said.
“This new positive outlook from Fitch Ratings — indicating another upgrade within the next year or two — shows we continue to be on the right path on behalf of our customers,” Falcone said.
Falcone discussed the factors behind rating agencies giving LIPA a series of rating upgrades in recent years in an episode of the American Public Power Association’s Public Power Now podcast.
Rating agencies have not only recognized LIPA’s success at deleveraging its balance sheet, but also the fact that the public power utility has seen significant improvement in the areas of customer satisfaction and reliability, Falcone said in an interview with APPA in 2000.
Fitch Cites Leverage Improvement
Fitch said that despite the challenges related to the coronavirus pandemic and Tropical Storm Isaias that hit Long Island in August 2020, leverage, as measured by net adjusted debt-to-adjusted funds available for debt service (FADS), improved to 8.4x at year end 2020 from 8.8x the two years prior. The improvement was attributable, in part, to LIPA’s strategy of budgeting to achieve higher fixed obligation coverage, the rating agency said.
“Going forward, leverage ratios are expected to trend below 8.0x in 2023, consistent with a higher rating, as performance continues benefitting from LIPA’s revenue-decoupling mechanism (RDM) as well as modest but consistent rate increases designed to achieve higher fixed charge coverage,” Fitch said.
“LIPA’s very strong service area, more disciplined approach to rate setting and authorized RDM should sustain its very strong revenue defensibility and overall performance even through the periods of stress, further supporting its financial profile,” the rating agency said.
Fitch also said that anticipated benefits that could accrue as a result of renegotiating LIPA’s operating services agreement with LIPA’s system operator PSEG Long Island (PSEGLI) are factored in the rating. The changes were triggered by PSEGLI’s poor response to Tropical Storm Isaias and follow a number of investigations, LIPA’s notice to terminate the contract and an analysis of alternate options for managing its assets, Fitch noted.
LIPA’s estimated costs incurred for Tropical Storm Isaias were $307 million, but the net financial impact of the storm will be limited as a result of Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) reimbursements and other offsetting responses.
Fitch Rates LIPA Electric System Revenue Bonds “A”
Fitch also said that it assigned an “A” rating to the following LIPA bonds:
- Approximately $368 million electric system general revenue bonds (tax-exempt fixed rate) series 2021A;
- Approximately $175 million electric system general revenue bonds (mandatory tender, tax-exempt) series 2021B;
- Approximately $195 million electric system general revenue bonds (federally taxable) series 2021C
Proceeds from the series 2021A bonds will be used to fund system improvements, refund existing debt and pay the costs of issuance. Proceeds from the series 2021B and C bonds will be used to fund system improvements and to pay the costs of issuance. All of the bonds will be sold with a fixed interest rate. The series 2021A and B bonds will amortize through 2042 and 2051, respectively. The series 2021C bonds will mature on March 1, 2023.
In addition, Fitch affirmed the following LIPA ratings at “A:” Issuer Default Rating and approximately $3.9 billion senior-lien electric system revenue and refunding bonds.
California Grid Operator Calls For Electricity Conservation With Forecast Of High Temperatures
September 8, 2021
by APPA News
September 8, 2021
The California Independent System Operator (ISO) called for voluntary electricity conservation on Wednesday, Sept. 8, due to predicted high energy demand and tight supplies on the power grid.
With above-normal temperatures in the forecast for much of California and the West, the power grid operator was predicting an increase in electricity demand, primarily from air conditioning use, it noted on Sept. 7 in issuing a statewide Flex Alert that called for voluntary electricity conservation from 4 p.m. to 9 p.m.
During the Flex Alert time period, consumers are asked to lower their thermostats to 78 degrees or higher, if health permits, and take other voluntary measures that include avoiding the use of major appliances and unnecessary lights.
CAISO noted that in the past, reducing energy use during a Flex Alert has helped operators keep the power grid stable during tight supply conditions and prevented further emergency measures, including rotating power outages.
To take full advantage of all available supply, the ISO also issued a restricted maintenance operation (RMO) for Sept. 8 from noon to 9 p.m., notifying ISO participants to avoid taking grid assets offline for routine maintenance until the RMO is lifted.
Department of Energy Study Maps Out Path For Solar Energy Expansion on U.S. Grid
September 8, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 8, 2021
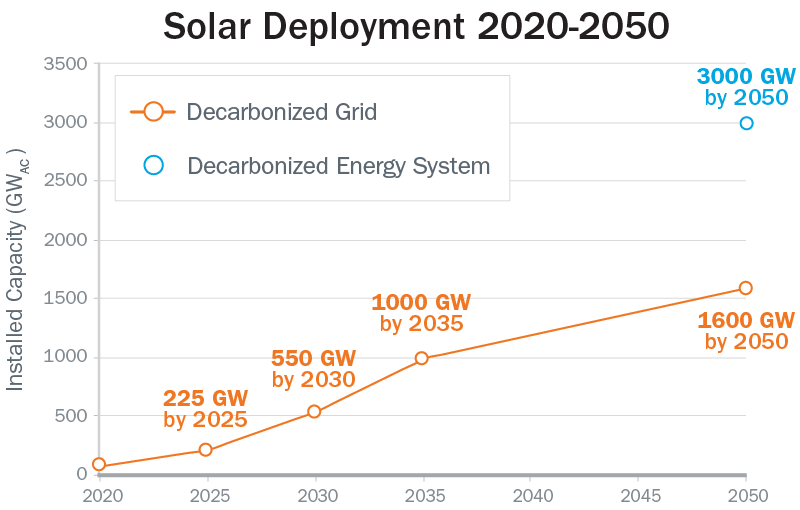
With aggressive cost reductions, supportive policies and large-scale electrification, solar energy could account for as much as 40% of the nation’s electricity supply by 2035 and 45% by 2050, according to a study released on Sept. 8 by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO) and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
To reach these levels, solar deployment will need to grow by an average of 30 gigawatts alternating current (GWac) each year between now and 2025 and ramp up to 60 GW per year between 2025 and 2030 — four times its current deployment rate — to total 1,000 GWac of solar deployed by 2035. By 2050, solar capacity would need to reach 1,600 GWac to achieve a zero-carbon grid with enhanced electrification of end uses, such as motor vehicles and building space and water heating.
Preliminary modeling shows that decarbonizing the entire U.S. energy system could result in as much as 3,200 GWac of solar due to increased electrification of buildings, transportation, and industrial energy and production of clean fuels.
Study Used Three Core Scenarios
The Solar Futures Study uses a suite of detailed power-sector models to develop and evaluate three core scenarios. The “Reference” scenario outlines a business-as-usual future, which includes existing state and federal clean energy policies but lacks a comprehensive effort to decarbonize the grid.
The “Decarbonization” (Decarb) scenario assumes policies drive a 95% reduction — from 2005 levels — in the grid’s carbon dioxide emissions by 2035 and a 100% reduction by 2050. This scenario assumes more aggressive cost-reduction projections than the Reference scenario for solar as well as other renewable and energy storage technologies, but it uses standard future projections for electricity demand.
And the “Decarbonization with Electrification” (Decarb+E) scenario goes further by including large-scale electrification of end uses.
The study also analyzes the potential for solar to contribute to a future with more complete decarbonization of the U.S. energy system by 2050, although this analysis is simplified in comparison to the grid-decarbonization analysis and thus entails greater uncertainty, DOE noted.
Even under the Reference scenario, installed solar capacity increases by nearly a factor of seven by 2050, and grid emissions decline by 45% by 2035 and 61% by 2050, relative to 2005 levels, DOE said. “That is, even without a concerted policy effort, market forces and technology advances will drive significant deployment of solar and other clean energy technologies as well as substantial decarbonization,” the study said.
The study said that the target-driven deep decarbonization of the grid modeled in the Decarb and Decarb+E scenarios yields more extensive solar deployment, similarly extensive deployment of wind and energy storage, and significant expansions of the U.S. transmission system.
In 2020, about 80 gigawatts (GW) of solar, on an alternating-current basis, satisfied around 3% of U.S. electricity demand. By 2035, the decarbonization scenarios show cumulative solar deployment of 760–1,000 GW, serving 37%–42% of electricity demand, with the remainder met largely by other zero-carbon resources, including wind (36%), nuclear (11%–13%), hydroelectric (5%–6%), and biopower/geothermal (1%).
By 2050, the Decarb and Decarb+E scenarios envision cumulative solar deployment of 1,050–1,570 GW, serving 44%–45% of electricity demand, with the remainder met by wind (40%–44%), nuclear (4%–5%), hydropower (3%–5%), combustion turbines run on zero-carbon synthetic fuels such as hydrogen (2%–4%), and biopower/geothermal (1%). Sensitivity analyses show that decarbonization can also be achieved via different technology mixes at similar costs, the DOE noted.
Although the study emphasizes decarbonizing the grid, the Decarb+E scenario envisions decarbonization of the broader U.S. energy system through large-scale electrification of buildings, transportation, and industry. In this scenario, electricity demand grows by about 30% from 2020 to 2035, owing to electrification of fuel-based building demands (e.g., heating), vehicles, and industrial processes. Electricity demand increases by an additional 34% from 2035 to 2050. By 2050, all these electrified sectors are powered by zero-carbon electricity. In this scenario, the combination of grid decarbonization and electrification abates more than 100% of grid CO2 emissions relative to 2005 levels.
With respect to the broader U.S. energy system, the Decarb+E scenario reduces CO2 emissions by 62% in 2050, compared with 24% in the Reference scenario and 40% in the Decarb scenario. The 38% residual in the Decarb+E scenario reflects emissions from direct carbon-emitting fossil fuel use, primarily for transportation and industry.
“We do not model elimination of these remaining emissions in detail, but a simplified analysis of 100% decarbonization of the U.S. energy system by 2050 shows solar capacity doubling from the Decarb+E scenario — equating to about 3,200 GW of solar deployed by 2050 — to produce electricity for even greater direct electrification and for production of clean fuels such as hydrogen produced via electrolysis.”
Additional Key Findings
Additional key findings of the study include, among others, the following:
- Achieving the decarbonization scenarios requires significant acceleration of clean energy deployment;
- Continued technological progress in solar—as well as wind, energy storage, and other technologies—is critical to achieving cost-effective grid decarbonization and greater economy-wide decarbonization;
- Solar can facilitate deep decarbonization of the U.S. electric grid by 2035 without increasing projected 2035 electricity prices if targeted technological advances are achieved;
- For the 2020–2050 study period, the benefits of achieving the decarbonization scenarios far outweigh additional costs incurred;
- Maintaining reliability in a grid powered primarily by renewable energy requires careful power system planning; and
- Although land acquisition poses challenges, land availability does not constrain solar deployment in the decarbonization scenarios
In addition, the study said that challenges must be addressed so that solar costs and benefits are distributed equitably. “Low- and medium-income communities and communities of color have been disproportionately harmed by the fossil-fuel-based energy system, and the clean energy transition presents opportunities to mitigate these energy justice problems by implementing measures focused on equity,” the study said. The study “explores measures related to the distribution of public and private benefits, the distribution of costs, procedural justice in energy-related decision making, the need for a just workforce transition, and potential negative externalities related to solar project siting and disposal of solar materials.”
Solar Futures Study Is Third In A Series Of Studies
The Solar Futures Study is the third in a series of vision studies from SETO and NREL, preceded by the SunShot Vision Study (2012) and On the Path to SunShot (2016).
While the previous studies focused on the impacts of low-cost solar technologies on the economy, this study dives into solar energy’s role in a decarbonized grid and provides analysis of future solar technologies, the solar workforce, and how solar energy might interact with other technologies like storage.
Peninsula Clean Energy Will Receive 35 MW Of Geothermal Power Under PPA
September 7, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 7, 2021
Starting in July 2022, California community choice aggregator (CCA) Peninsula Clean Energy will receive 35 megawatts (MW) of geothermal power from The Geysers, a 725-MW complex run by Calpine Corporation and located 70 miles north of San Francisco.
The power purchase agreement is Peninsula Clean Energy’s first to involve geothermal.
The 15 geothermal power plants at The Geysers stretch across 45 acres in Sonoma and Lake Counties and are responsible for providing nearly one-tenth of the renewable power produced annually in California.
The geothermal power from The Geysers will bring Peninsula Clean Energy another step toward the CCA’s ultimate goal of providing 24/7 renewable power to its customers, it noted.
Peninsula Clean Energy is on track to deliver electricity that is 100 percent renewable by 2025 and has earned investment grade credit ratings from Moody’s and Fitch.
Peninsula Clean Energy is the official electricity provider for San Mateo County, Calif., and, beginning in 2022, for the City of Los Banos, Calif.
The American Public Power Association has initiated a new category of membership for CCA programs.
City Council Vote Marks Next Step in LADWP’s Transition To 100 Percent Carbon-Free Energy
September 7, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 7, 2021
The Los Angeles City Council on Sept. 1 directed the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) to take the steps necessary for the city to achieve 100 percent carbon-free energy by 2035.
“This is truly a great day for Los Angeles that puts our city firmly in a leadership position among world cities working to decarbonize the planet,” said Marty Adams, LADWP’s General Manager and Chief Engineer, in a statement. “Our city has set a goal of 100% carbon-free energy by 2035 and we’re here to tackle the challenge and say, LADWP is all in.”
Councilmembers voted on a motion introduced by Councilmembers Paul Krekorian and Mitch O’Farrell. The motion noted that LADWP is going to prepare a strategic long-term resource plan, which will determine the optimal pathway to achieve the 100 percent clean energy goal. It will align with LADWP’s priorities for ensuring power reliability, sustainability, affordability and equity for LADWP’s customers.
The council also approved a related motion from O’Farrell and Krekorian that will create a strategic plan for equitable workforce hiring, which is aimed at ensuring a just transition to thousands of green new jobs.
Results Of NREL Study Released Earlier This Year
Earlier this year, results of a years-long analysis were released by the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), which found that meeting Los Angeles’ goal of reliable, 100% renewable electricity by 2045, or even 2035, is achievable with rapid deployment of wind, solar, storage, and other renewable energy technologies this decade.
The results of the study were released by Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti, United States Secretary of Energy Jennifer Granholm, LADWP Board of Water and Power Commissioners President Cynthia McClain-Hill, Adams, a number of Los Angeles City Council members and Dr. Martin Keller, Executive Director, NREL. They participated in a virtual press event to release the Los Angeles 100% Renewable Energy Study, known as LA100.
More recently, in June, LADWP said it would launch a comprehensive and inclusive, community-driven effort to achieve a just and equitable 100% carbon-free future for all communities of Los Angeles. LADWP’s Board of Water and Power Commissioners on June 23 authorized the public power utility to move forward with LA100 Equity Strategies, which aims to incorporate community-driven and equitable outcomes into the goals of the LA100 study completed by NREL.
LADWP Officials Appear Before Council
Prior to the council’s vote, Adams and Reiko Kerr, LADWP Senior Assistant General Manager-Power System Engineering, Planning, and Technical Services, offered remarks on LA100 and took questions from councilmembers.
“When you talk to anybody in the Department of Energy, they will tell you the only thing they’re talking about in D.C. is the City of Los Angeles and the LA100 study,” Adams told councilmembers. “This is a huge win for the city,” Adams said.
There is also a LA100 next steps plan. “This is the parts and pieces. This is where we’re looking at exactly what we have to complete in the next ten years to reach that clean energy future goal.”
LADWP’s strategic long-term resource plan is a 25-year plan that is examining what LADWP’s staffing and human resources plan needs to be because there will be a “tremendous need for expanding our workforce to get this work done,” he said. The plan is also looking at “how these projects have to dovetail together to make sure we don’t have outages or instability in the system in the meantime.” Operation and maintenance are another component of this plan “to make sure that the power reliability that the city of L.A. has enjoyed not only continues but improves all through the process,” Adams said.
“I promise you that we’re going to take this very seriously and make this happen,” Adams told councilmembers prior to the vote.
Adams discussed LA100 in an American Public Power Association Public Power Now podcast earlier this year.
“This vote is a vote that will be transformative to the future of the City of Los Angeles,” Councilmember Krekorian said. “This is a vote that will help shape the future of the economy of Southern California. This is a vote that will create thousands and thousands of new, good jobs. It’s a really big deal.”
In a news release related to the vote, Krekorian noted that LADWP has already taken significant steps toward achieving its 100 percent clean energy goal, laying the groundwork to accommodate 580,000 electric vehicles and adding over 1,000 megawatts of energy storage by 2030.
At the council meeting on Sept. 1, Krekorian asked Adams and Kerr to talk about how LADWP is poised to take advantage of federal and state government infrastructure investment funding opportunities “to be able to begin building the things that we need to build” to get to 100 percent carbon-free energy, to upgrade the transmission and distribution infrastructure “and otherwise take advantage of that funding that’s available.”
Kerr said that green hydrogen has received a lot of attention at both the federal and state level “and so we’ve been in discussions for funding for that. At the state level, there is potential opportunity for green hydrogen and that has multiple benefits.”
She noted that green hydrogen allows firm dispatchable generation that has carbon-free emissions “for those times where you either have an emergency or you lose import capability or there’s no wind and no solar to ensure that we have reliability.” (A recent APPA report on hydrogen notes that green hydrogen or renewable hydrogen is made from renewable energy via electrolysis).
Green hydrogen also provides long duration storage, Kerr noted. She said that this is very important “because when you look at the over generation of renewables in the springtime” there is a large amount of over generation because that time of year is when loads are low, “but you’re really building your generation profile for those peak periods during the summer, so you have all that excess. If we can use that to create the green hydrogen in the spring, you can use that hydrogen to store it” over multiple months until needed in the summer. “We’ll be looking for state funding,” she said.
Kerr noted that LADWP has issued a request for information for green hydrogen in-basin, so there are state opportunities for local green hydrogen.
In May 2021, LADWP joined a coalition that aims to bring down the cost of green hydrogen. LADWP, along with the Green Hydrogen Coalition and other partners, launched HyDeal LA, a collaboration of developers, green hydrogen off-takers, integrators, equipment manufacturers, investors, and advisors. The group aims to work together to bring the cost of green hydrogen down to $1.50 per kilogram in the Los Angeles Basin by 2030 by creating a commercial green hydrogen cluster at scale.
Joining HyDeal LA marks another significant initiative around green hydrogen for LADWP, which is leading the conversion of the Intermountain Power Project in Delta, Utah to the world’s first turbine intentionally designed and built to operate with a blend of 30% green hydrogen and 70% natural gas when the plant goes into operation in mid-2025. It will be designed to scaleup to 100% carbon free green hydrogen by 2035.
LADWP has some projects that could be considered shovel ready, noted Adams, who went on to say that the utility is working to try to streamline environmental processes because a lot of the costs for the projects relate to “just getting them off the ground, getting them engineered and getting them approved to be constructed.”
Adams said that “We will continue to seek all avenues for resources,” adding that there is “a lot of federal money out there for construction, particularly infrastructure construction and so we are very much focused on getting whatever funds are available because all those funds then decrease the costs that ultimately go to our ratepayers.”
Study Finds Hydrogen Peakers Beat Batteries, But Not Gas Peakers
September 3, 2021
by Peter Maloney
APPA News
September 3, 2021
Hydrogen fuel could be a more economical solution to the intermittency of renewable energy resources than lithium-ion batteries, but it is not an economic match to natural gas-fired peaking plants at current market prices, according to a new report from researchers at the MIT Energy Initiative (MITEI).
Hydrogen is attracting a lot of interest as an alternative fuel for power peaking power plants. Several public power utilities, particularly on the West Coast, are exploring hydrogen as an alternative to natural gas and are looking at projects to produce so-called green hydrogen by using renewable resources to power electrolyzers that produce the gas from water. Utilities ranging from the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power and the Northern California Power Agency to the Douglas County PUD and the Nebraska Public Power District have embarked on hydrogen pilot projects.
While there has been a rapid rise in the deployment of lithium-ion batteries to aid in the integration of intermittent resources such as wind and solar power, batteries are sized to produce power for hours at a time and are best used to address daily imbalances between electric supply and demand, the authors of the report in Applied Energy said. (The online version of the article was published in July; the print version is due out in October.)
The report’s authors, Drake Hernandez and Emre Gencer, used a least cost of energy (LCOE) approach to analyze the economics of meeting seasonal energy imbalances, comparing hydrogen-fired gas turbines (HFGT) and lithium-ion battery systems (LI).
They found that the LCOE associated with meeting seasonal energy imbalances is $2,400 per megawatt hour (MWh) using a hydrogen-fired gas turbine and $3,000/MWh using a lithium-ion battery system. If a gas turbine is fired with “blue” hydrogen, that is, hydrogen produced by reforming natural gas, the average LCOE decreases to $1,560/MWh. On average, reforming hydrogen rather than electrolytic hydrogen turned out to be the cheapest option for replacing peaking plants, the report found.
Nonetheless, “the power prices required to justify investment in an HFGT to replace a natural gas-fired gas turbine are considerably higher than those seen in the market today,” the authors said.
“Our study’s essential takeaway is that hydrogen-fired power generation can be the more economical option when compared to lithium-ion batteries—even today, when the costs of hydrogen production, transmission, and storage are very high,” Hernandez said in a statement.
The study also looked at the economics of retrofitting natural gas plants to burn hydrogen, as opposed to building entirely new facilities, and found the price for converting a fossil fuel plant to burn hydrogen is high and such conversions likely would not take place until more sectors of the economy embrace hydrogen, either as a transportation fuel or for varied manufacturing and industrial purposes.
The authors also noted that “enormous investments” would be necessary to expand hydrogen production facilities to meet grid-scale needs. “With any of the climate solutions proposed today, we will need a carbon tax or carbon pricing; otherwise, nobody will switch to new technologies,” Gencer said in a statement.
The study looked at all peaking plants in California, using 2019 as the base year. The researchers looked at the costs of running natural gas-fired peakers, defined as plants operating 15 percent of the year to make up for intermittent energy resources. They also determined the amount of carbon dioxide released by those plants and the expense of abating those emissions.
The American Public Power Association recently issued a report that offers a perspective on where the emerging hydrogen market is in the U.S. and globally, what is driving the growing interest in hydrogen and what obstacles are preventing hydrogen technology from being able to scale-up.
Burlington Electric Department And Mayor Propose Net Zero Energy Revenue Bond
September 3, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 3, 2021
Burlington, Vermont, Mayor Miro Weinberger and public power utility Burlington Electric Department (BED) have proposed a new, $20 million Net Zero Energy Revenue Bond that would accelerate progress toward Burlington’s climate goals, while reducing upward rate pressure for BED customers, BED reported on Sept. 2.
In addition, the mayor and BED announced that BED’s green stimulus program would continue and that Moody’s Investors Service affirmed BED’s A3 rating.
The Net Zero Energy Revenue Bond, combined with a portion of BED’s annual General Obligation (GO) Bond, would make numerous investments, including:
- $17.5 million to support projects that help advance progress toward the net zero energy goal;
- $7.8 million to fund grid upgrades that support reliability and manage new loads from strategic electrification;
- Renewable energy generation plant maintenance and upgrades;
- Investment in electric vehicle charging and demand response infrastructure; and
- Upgrades to technology systems to support new dynamic rates and load control
The Net Zero Energy Revenue Bond would reduce future rate pressure significantly for BED customers relative to a scenario where BED made these investments without the bond, BED noted.
Debt service on the revenue bond proposal and that portion of the GO bond used for strategic electrification would be supported by net revenue from strategic electrification projects between Fiscal Year 2023 and Fiscal Year 2025 that will contribute approximately 40 percent of BED’s obligation over the 20-year debt service life of the bonds and savings of $684,000 of BED’s debt service starting in Fiscal Year 2026, due to the maturity of existing bond debt.
Also, under a new Vermont Public Utility Commission (PUC) order approving a BED proposal, the utility will double funding at least through the end of Fiscal Year 2025 for strategic electrification, including continuing its green stimulus program.
The doubling of funding would be supported by approximately $5.3 million from BED’s annual GO Bond. This will reduce fossil fuel use through customer incentives for heat pumps, EVs, electric lawn care equipment, electric bikes, and more, as well as avoid over 47,000 tons emissions, equivalent to nearly 100,000 barrels of oil burned, compared to business as usual, BED said.
Meanwhile, Moody’s Investors Service affirmed BED’s A3 rating on outstanding revenue bonds on August 16, 2021, with a stable outlook. Moody’s cited BED’s 100 percent renewable power supply, the diverse local economy in Burlington, and recent action to adjust rates for the first time in 12 years as positive indicators.
Among the first of its kind nationwide, the Net Zero Energy Revenue Bond proposal was recommended by the Burlington Electric Commission by a 5-0 vote. The Burlington Board of Finance and City Council will consider the proposal for placement on the November ballot at their September 13 meetings.
In September 2019, Weinberger, joined by BED General Manager Darren Springer, City Director of Sustainability Jennifer Green, and other stakeholders, released the City’s Net Zero Energy Roadmap. More than a year in the making, the roadmap studies what it will take for Burlington to accomplish its goal to become a Net Zero Energy city by 2030, and identifies four key pathways to get there.
Springer discussed the roadmap in an episode of the American Public Power Association’s Public Power Now podcast.
Details On Green Stimulus Program
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, Weinberger announced that a new green stimulus program would be launched using existing funds to support a range of expanded and new initiatives to help boost both the city’s economic recovery from the pandemic and its transition to becoming a Net Zero Energy city.
In response, BED worked quickly last year to implement the green stimulus, which launched on June 1, 2020 and offers incentives for technologies including heat pumps, heat pump water heaters, electric vehicles, and more.
The success in 2020 of the green stimulus led the mayor and BED to announce that the green stimulus program initiatives have been extended into 2021 and will remain available through year’s end or until funding is exhausted.
San Diego County Board of Supervisors Approves Community Choice Energy Move
September 1, 2021
by Paul Ciampoli
APPA News Director
September 1, 2021
The County Board of Supervisors for San Diego, Calif., voted on Aug. 31 to authorize the county to join a community choice energy (CCE) program called San Diego Community Power.
The CCE launched in March and includes the cities of Chula Vista, Encinitas, Imperial Beach, La Mesa and San Diego.
The county will become part of a joint powers authority which governs the CCE. CCEs are also known as community choice aggregators (CCAs).
Community choice allows cities and counties to buy electricity, including renewable energy like solar and wind for residents and businesses. CCEs offer customers in the county’s unincorporated areas an alternative to buying power from investor-owned San Diego Gas and Electric (SDG&E). SDG&E would still provide transmission and delivery services, as well as billing.
The CCE could provide residents competitive utility rates and cost savings compared to SDG&E, and also offer more renewable power, the board of supervisors said.
Currently, there are 24 CCEs operating throughout the state including two in San Diego County, San Diego Community Power and the Clean Energy Alliance. The alliance members include Carlsbad, Del Mar and Solana Beach. In all, the state’s CCEs serve 11 million customers.
San Diego Community Power is expected to begin serving county customers in spring 2023.
Association offers new CCA program membership category
The American Public Power Association has initiated a new category of membership for CCA programs.
